
Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex YouTube
0:00 / 2:24 Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex Pyramid of Potential Inc. 5.91K subscribers 109K views 10 years ago Kathy Johnson, M Ed describes the Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex, and how it impacts.

Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex Dyslexic Strategies
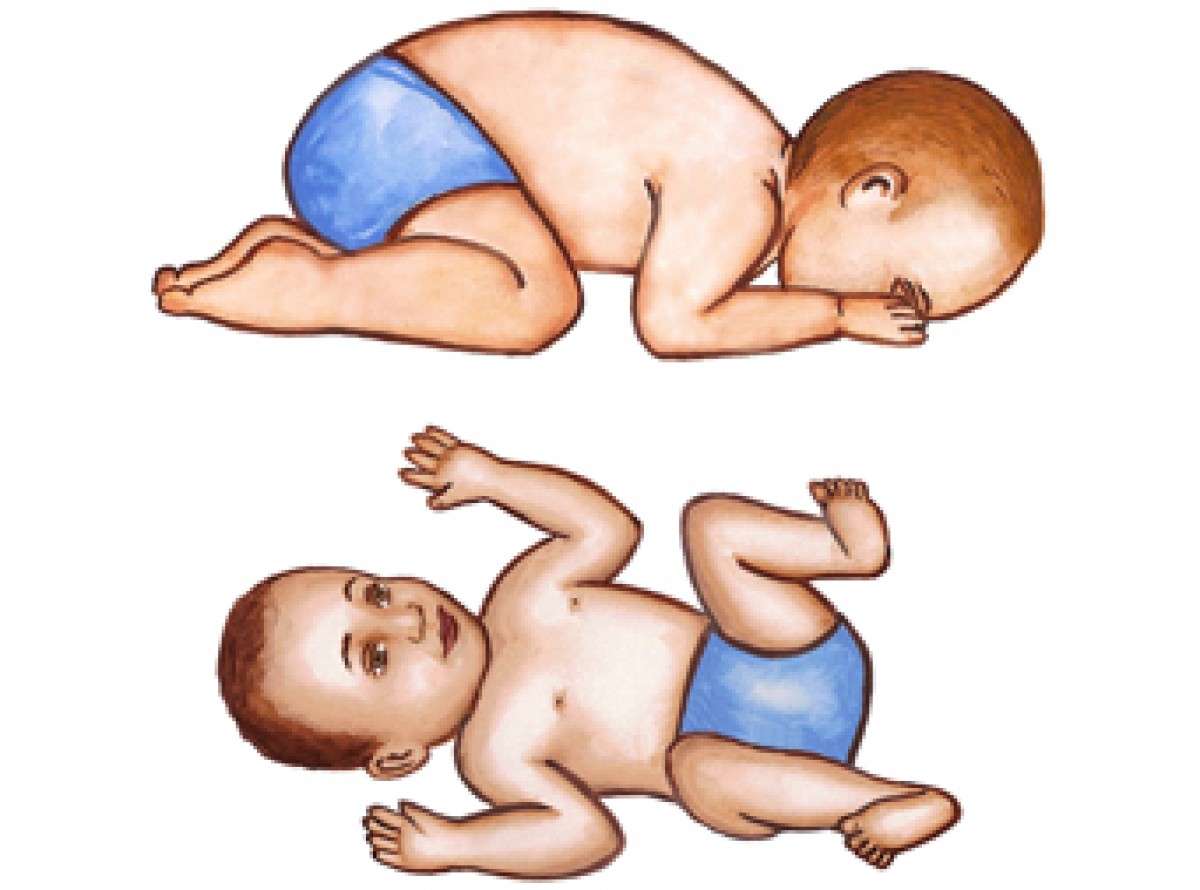
Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR) Trigger—Forward TLR When lying on the back, the baby's head moves forward, above the level of the spine. Response to Trigger Arms and legs pull up and close to the body Trigger—Backward TLR When laying on the back, the baby's head moves backward, below the level of the spine. Response to Trigger

Pin on Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR)
The grasping reflex described above is one of the motions that babies produce involuntary: Your baby's central nervous system (CNS) — their brain and spinal cord — automatically orders your.

Nbcot Exam Prep, Primitive Reflexes, Neonatal, Learning Disabilities
Tonic Neck Reflex - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Primitive reflexes are innate, automatic motor patterns and reactions emerging during fetal life until after birth crucial for an infant's survival. These reflexes are being integrated and replaced gradually in term infants into higher-level righting, support, and protective postural reactions.

Testing for a persistent TONIC LABYRINTHINE REFLEX (TLR) YouTube
The Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR) is a primitive reflex that is present in newborn babies and is responsible for helping them maintain balance and posture. It is triggered by stimulation of the labyrinthine system, which is made up of the inner ear and the vestibular nerve. The TLR is responsible for helping babies learn to roll over, sit up.

Retained Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex Solve Learning Disabilities
The Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR) is a reflex that plays a crucial role in the development and movement of individuals. Understanding the TLR is essential for parents, caregivers, and professionals working with children, as it can significantly impact their overall development and motor skills.

tlr ext Reflexes, Tonic, Helping kids
Tonic labyrinthine reflex - Physiopedia: This source provides a more detailed description of the Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex, its emergence and integration, its position, stimulus and response, its clinical implication, and its physiotherapy management. It also includes some videos and images to illustrate the TLR and its testing.
Manuals & Tools Masgutova store, manuals, books, dvds, music, reflex
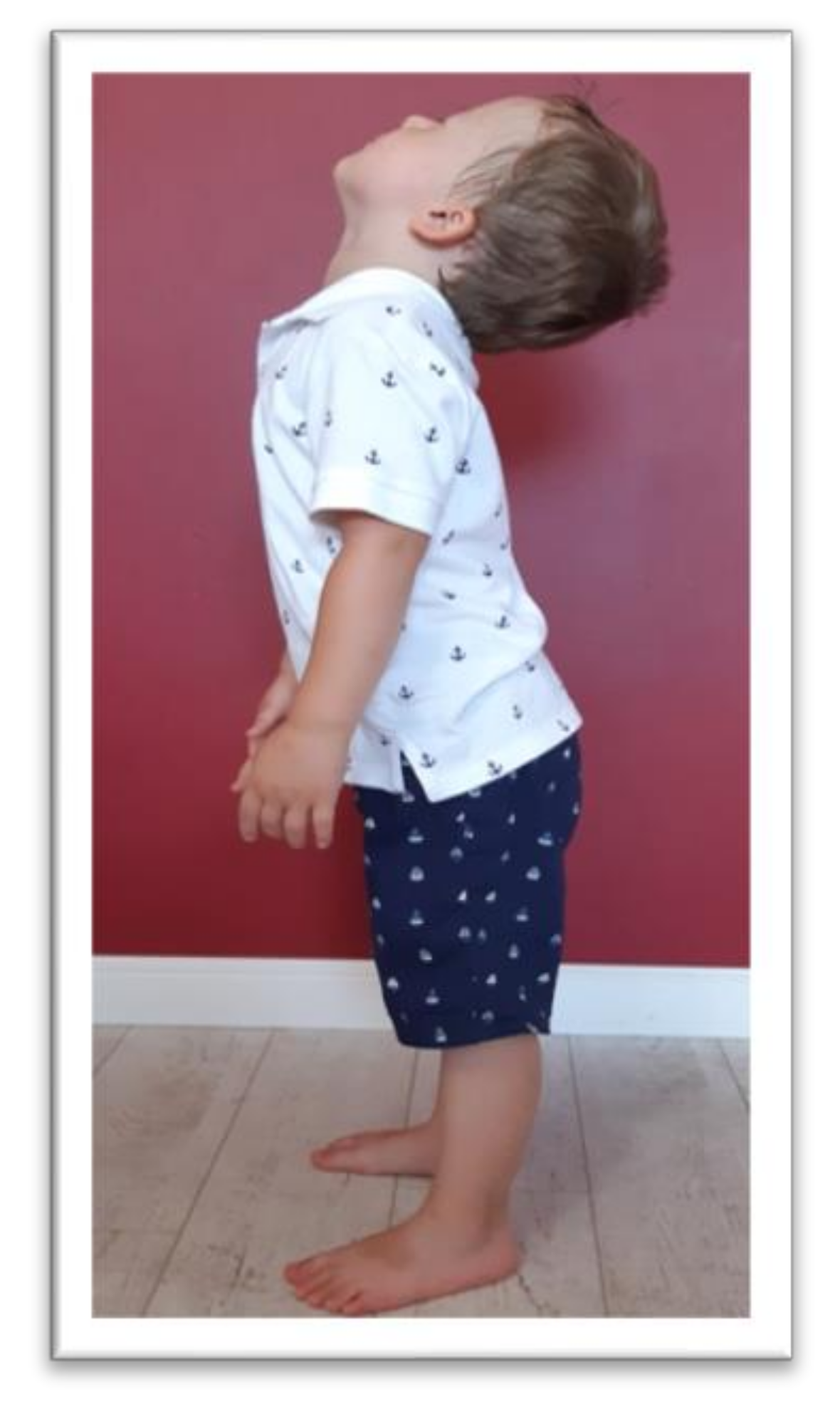
Testing for Persistent Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex [edit | edit source] To test for the Tonic labyrinthine Reflex, the child should stand with feet together and arms beside the body. The child will then lift the head up, close the eyes and hold for 10 seconds. After 10 seconds, the child should look down slowly and hold for another 10 seconds.

Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR) is the response to the change of the
The Tonic Labyrinthine reflex (TLR) affects spatial judgment, muscle tone, balance and, if present, can induce motion sickness.. The Asymmetrical Tonic Neck reflex (ATNR) affects midline.

trlreflex.jpg Occupational therapy kids, Primitive reflexes, Reflexes
The Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR) helps with the development of neck and head control, increases muscle tone, improves posture and balance, and develops the proprioceptive and balance senses. The Landau Reflex helps with coordination between the upper and lower parts of the body. Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR)

Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex Test YouTube
The tonic labyrinthine reflex ( TLR) is a primitive reflex found in newborn humans.

Retained Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex Solve Learning Disabilities
The Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex is a reflex that emerges at birth and is expected to have integrated within 2-4 months after birth. The tonic labyrinthine refl.

Retained Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex Solve Learning Disabilities
What is Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex? TLR is a primitive reflex in newborns. Normally, a baby spends time on their tummy with head and arms up and out. While doing this, a baby develops the muscles in their neck, shoulders, and back. These muscles are necessary for later stages of development.

Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (21/60) YouTube
TLR: The Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex •The basis for head management •Helps prepare an infant for rolling over, creeping, crawling, standing and walking •Initiates when you tilt an infant's head backwards while placed on the back causing legs to stiffen, straighten and toes to point. •Hands also become fisted and elbows bend.

IJERPH Free FullText Primitive Reflex Activity in Relation to the
The tonic labyrinthine reflex is a primitive reflex found in newborn humans. With this reflex, tilting the head back while lying on the stomach causes the back to stiffen and even arch backwards, the legs to straighten, stiffen, and push together, the toes to point, the arms to straighten . The reverse happens to arms and legs with neck flexion.
Benefits of the Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR) for Optimal Childhood
Retained Tonic LABYRINTHINE reflex. This reflex typically integrates around 4 months old, but if it persists, the following may occur: Difficulties judging space, speed, depth, and distance. Toe walking. Discoordination in simultaneous movements, such as walking or swimming. Avoiding lying on their stomach.